WHAT IS BIODIESEL?
Biodiesel is a biofuel obtained from the conversion of vegetable oils extracted from oilseeds, such as soybean, palm and sunflower, or from animal fat from cattle, swine, poultry, etc. After undergoing purification processes to meet quality specifications, biodiesel is used in diesel cycle engines as a partial or total substitute for mineral diesel (diesel A).
National Program
for the Production
and Use of Biodiesel
The National Program for the Production and Use of Biodiesel (PNPB) was launched in 2005, with the voluntary blending of 2% biodiesel (B2) in commercial diesel (diesel B). This biodiesel content became mandatory as from 2008 and is currently at 14% (B14). According to the official schedule of the National Energy Policy Board (CNPE), linked to the Ministry of Mines and Energy (MME), this proportion should reach 15% (B15) by 2025.

Trading
Following the guidelines of CNPE Resolution 14/2020, the trading of biodiesel to meet the mandatory biodiesel percentage requirement established by Law 13,033/2014 started, as of January 1, 2022, to take place under supply agreements validated by the Brazilian Petroleum, Natural Gas and Biofuels Agency (ANP) or via transactions in the spot market.
Climate Change
Brazilian biodiesel is capable of reducing greenhouse gas emissions by at least 80% when compared to fossil diesel, according to data from the Energy Research Company (EPE).
With more biodiesel, engines, machinery and equipment use less polluting fuels. In addition to bringing direct environmental benefits by mitigating part of the CO₂ emissions in the fuel matrix, biodiesel contributes to Brazil’s progress in performing climate change agreements.
The production of biodiesel between 2008 and 2023 was 67.6 billion liters. This volume replaced the import of petroleum-derived diesel.
Biodiesel avoided
the emission of
130 million
tons of CO₂
between 2008 and 2022
Public Health
The use of biodiesel reduces the emission of polluting gases and harmful substances into the atmosphere, contributing to the health of the population and reducing social costs from hospitalizations and sick leaves due to cardiorespiratory illnesses.
The study “Impact on Human Health by the Use of Biofuels in the Metropolitan Region of São Paulo,” by EPE, indicates that, according to the World Health Organization (WHO), more than four million people die prematurely every year as a result of health problems caused by air pollution.
Each additional percentage point of the biodiesel mixture in diesel prevents 244 deaths per year and reduces social costs by R$178 million.
The GDP of the soybean and biodiesel production chain is expected to reach R$ 422 billion in 2024, representing 18% of the Brazilian agribusiness GDP and 3,9% of the country’s total GDP
GDP, Employment and Labor
In the first quarter of 2024, the population employed in the soybean production chain totaled 2.28 million people. That represents 9.69% of the population employed in the agribusiness sector and 2.28% of the country’s total population employed.
The workforce in the soybean chain is reasonably formalized. People working under the Brazilian Labor Code (CLT) accounted for 46% of the total employed individuals. Women account for 35%, and the level of education was higher if compared to that of the agribusiness sector.
Regional Development
The production of biodiesel is linked to activities that are major job creators.
The industrial park promotes regional social and economic development, thus improving the development index of the small regions served, since most of these units are located outside large urban centers.
Thus, for every additional R$1 in the biodiesel production activity, 33 jobs are added to the economy.
More than 14,000 people are directly employed in the production of biodiesel alone, and they are paid 40% more than the average salary of jobs in the Brazilian agribusiness industry.
68 plants
16 states
14.000
people directly
employed in
the production
of biodiesel
Family Farming
Biodiesel stimulates income generation in the countryside, with the promotion of family farming through the Social Fuel Seal.
Created by the Ministry of Agriculture (MAPA), the program benefits over 76,000 families (around 330,000 people), providing technical support and agricultural extension to farmers and assisting them with market access and distribution of their production.
This initiative establishes mechanisms for integrating biodiesel plants with family farming through the acquisition of raw materials (grains, live animals, vegetable oils and animal fats) and promotion activities (donations of seeds and inputs, etc.), with the signing of purchase guarantee agreements, providing income and revenue predictability to farmers.
Learn about the program

Added Value
The production of biodiesel stimulates soybean processing.
Thus, it indirectly benefits the production of animal protein, which requires a large amount of soybean meal. This soybean byproduct is used as raw material for the production of feed for cattle, poultry and fish. Each additional percentage point of biodiesel in the blend represents higher meal production, resulting in lower production costs for the chicken, pork, eggs and fish sectors, with impact on the Extended National Consumer Price Index (IPCA).
Use of Residual Cooking Oil
More than an energy alternative, the use of this source contributes to environmental protection and social and economic development.
When disposed of properly, used cooking oil prevents damage to nature and, since it is considered a high-value waste, it is a source of income for those who work in cooperatives and the recycling industry. This reinforces the importance of proper collection and disposal of the product, which after being recycled is transformed into hygiene items, paints, varnishes, biodegradable soap, animal feed and biodiesel. Note that the production processes of cooking oil meet all sustainability requirements, delivering a high-quality product to consumers. However, to complete the circular economy cycle and reduce environmental impacts, the used oil must be properly disposed of.
Over 126,000 m³ of used frying oil was used as raw material for the production of biodiesel in Brazil in 2023.
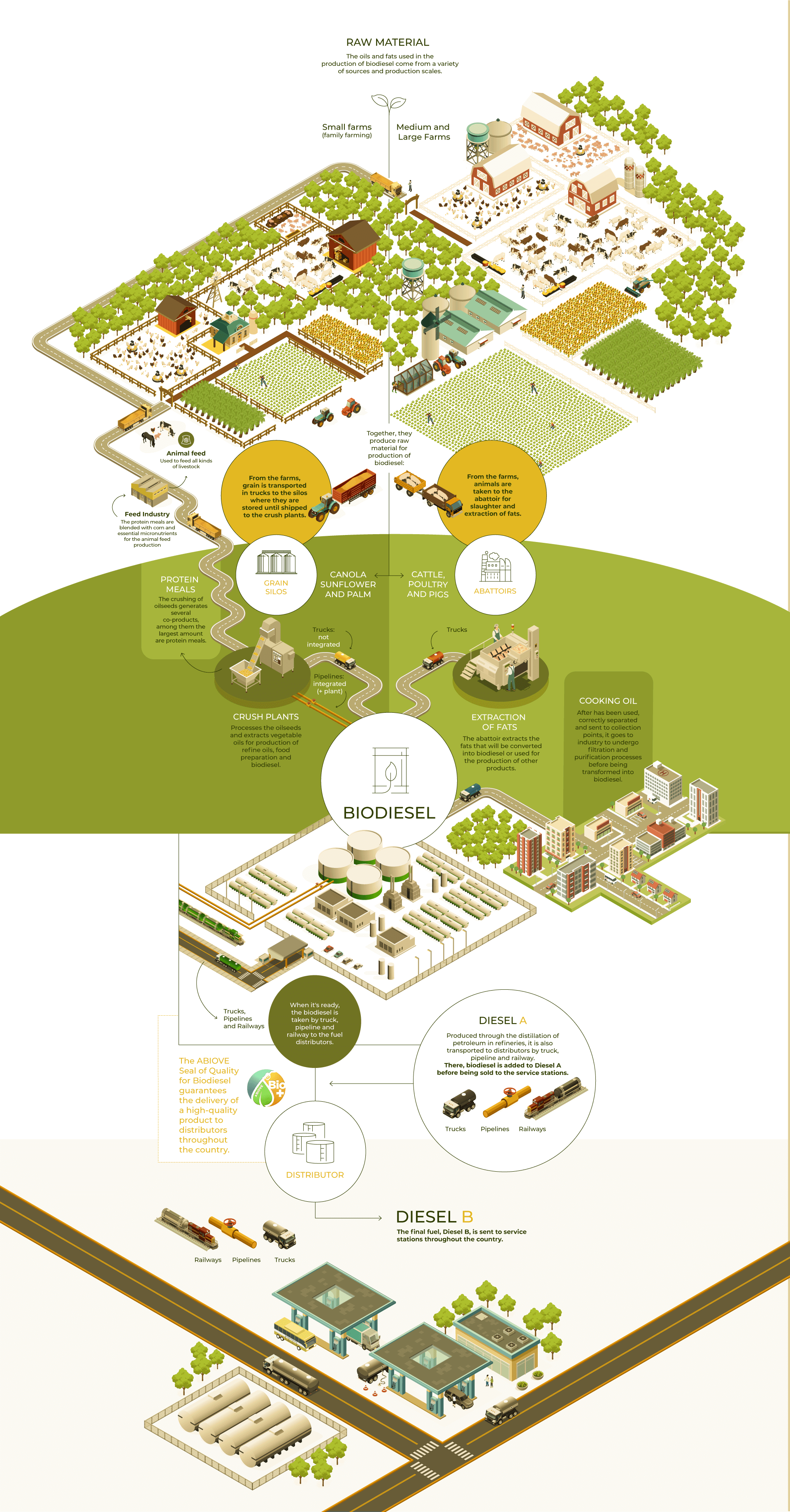
Production Chain
Check out the infographic
illustrating the operation of
the biodiesel production
chain in Brazil